Why did bitcoin increase in value
Contents:
The U. Library of Congress publishes a detailed report on its regulatory status around the world. Bitcoin is a volatile investment when considering the basis of the currency's price. When the currency was first launched in , it had no official price because it was not being sold. However, when the first exchanges began to appear, a price developed. Bitcoin's price at first was small—just a few cents, and it wasn't even being tracked like stocks are in the market.
As an example, you could look up the price of Bitcoin on the internet, and you might find two different prices. If you used Coindesk.
Why is Bitcoin price dropping? Drop in cryptocurrency price explained as bond yields increase
Part of the reason for all the different values is where the data comes from. Bitcoin is never traded in one place. Instead, it is traded on multiple exchanges, all of which set their own average prices, based on the trades being made by the exchanges at a given time. Indexes gather together prices from several exchanges and average them out, but not all of the indexes use the same exchanges for their data. If you want to buy and sell Bitcoin, you have to choose a particular exchange, which will have its average price.
The price of Bitcoin fluctuates at any given moment, depending on which exchange the information comes from. The price of Bitcoin is very volatile, partly due to the liquidity the ability to quickly buy and sell of the currency. The amount of bitcoins flowing through the market at any point in time gives investors the ability to enter and exit positions quickly.
5 reasons why bitcoin cryptocurrency prices are on the rise
If people are trading a high number of a particular asset, it becomes harder for one person or event to shift that price in any single direction. Think of it as a stream of water—you can redirect a small stream by putting down a few planks of wood. With fiat currencies like the U. With Bitcoin, trading volumes are small in relation to the rest of the assets being traded daily—which means that single events can make a bigger difference.
The Bitcoin market is influenced by many events. If it is leaked that a large government is uncertain about how to regulate Bitcoin—as occurred in China—the price can fall.
- convert doge to btc.
- History of bitcoin?
- Why Does the Price of Bitcoin Keep Going Up?.
There are also other factors affecting Bitcoin prices. There are only so many bitcoins available, and they are produced at a predictable rate. The ownership of those bitcoins is unevenly distributed—some Bitcoin giants have vast hoards of the currency in their wallets digital storage. That, combined with liquidity, makes it easy for people to manipulate the market. Research has shown that bitcoin's market price is closely related to its marginal cost of production.
The more popular an exchange becomes, the easier it may draw in additional participants to create a network effect. And by capitalizing on its market clout, it may set rules governing how other currencies are added. The rapid rise in the popularity of bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies has caused regulators to debate how to classify such digital assets. This confusion over which regulator will set the rules for cryptocurrencies has created uncertainty—despite the surging market capitalizations.
Furthermore, the market has witnessed the rollout of many financial products that use bitcoin as an underlying asset, such as exchange-traded funds ETFs , futures, and other derivatives. This can impact prices in two ways. First, it provides bitcoin access to investors who cannot afford to purchase an actual bitcoin, thus increasing demand.
Because bitcoin is not governed by a central authority, it relies on developers and miners to process transactions and keep the blockchain secure. Software changes are consensus-driven, which tends to frustrate the bitcoin community, as fundamental issues typically take a long time to resolve. The issue of scalability has been a particular pain point. The number of transactions that can be processed depends on the size of blocks, and bitcoin software is currently only able to process approximately three transactions per second.
The community is divided over the best way to increase the number of transactions.
- bitcoin core bandwidth.
- Bitcoin (BTC) price history from 2013 to March 26, 2021?
- soon huat bitcoin.
Past bitcoin hard forks have included bitcoin cash and bitcoin gold. Bitcoin's value is largely dependent on its supply and the market's demand for it.
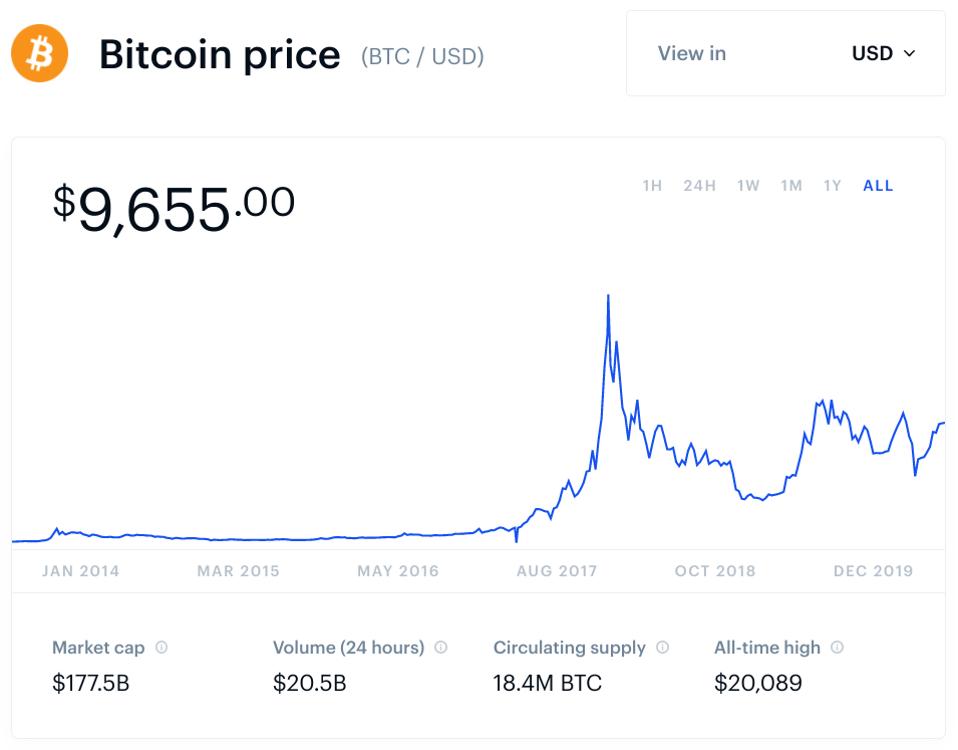
Its value is also attributed to other factors, such as alternative digital currencies— including their supply and price—availability, and rewards for mining. As bitcoin nears its maximum limit, demand for it increases. The increased demand and limited supply push the price per bitcoin upward. Also, more institutions are investing in bitcoin and accepting it as a form of payment, thereby increasing its utility and making it a preferred medium of exchange among consumers.
Bitcoin is relatively safe due to cryptography and robust protocols and readily available through several exchanges. Also, you need not purchase a full bitcoin to have ownership of it.

Fractional shares are available, increasing its attractiveness and value. Unlike stock, bitcoin does not represent ownership in a company or entity. Bitcoin miners earn rewards for completing blocks of verified transactions, and owners of bitcoin make money as the price per coin increases. The demand for bitcoin is increasing, whereas its available supply is shrinking. This results in increased prices. Consumers, companies, and investors favor bitcoin for its profitability and its ability to hedge inflation. The resulting popularity contributes to increased demand, and thus an increased price.
Bitcoin's price fluctuates for various reasons, including media coverage, speculation, and availability. With negative press, some bitcoin owners panic and sell their shares, driving down the price. Vice versa with positive press. Also, when the volume of bitcoin sold on the market increases, the price decreases. As more institutions adopt bitcoin as an investment and medium of exchange, its price increases.
Why Do Bitcoins Have Value? · 1. Scarcity. The key to the maintenance of a currency's value is its supply. · 2. Divisibility. Successful currencies are divisible into. Another reason for Bitcoin's rise is the growing inflation of the U.S. dollar. While inflation is on average 2% each year, recent stimulus spending is poised to greatly.
Also, many people have eroded confidence in their fiat currency and seek alternative sources to store their money. Because bitcoin is decentralized and unregulated, it is a favorable alternative, thus driving up its price.
Key Takeaways Currencies have value because they can be used as a store of value and a unit of exchange. Digital Trends. Must Read. Past bitcoin hard forks have included bitcoin cash and bitcoin gold. Your Money. Bitcoin Bitcoin's Price History. The following piece sums up common factors affecting the value of digital currencies and indicators, reflective of their truthful value.
Since each individual's situation is unique, a qualified professional should always be consulted before making any financial decisions. Investopedia makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or timeliness of the information contained herein. Accessed March 15, Your Privacy Rights. To change or withdraw your consent choices for Investopedia.
At any time, you can update your settings through the "EU Privacy" link at the bottom of any page.
A functional and decentralised digital currency
These choices will be signaled globally to our partners and will not affect browsing data. We and our partners process data to: Actively scan device characteristics for identification. I Accept Show Purposes. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Part Of. Bitcoin Basics. Bitcoin Mining. How to Store Bitcoin. Bitcoin Exchanges. Bitcoin Advantages and Disadvantages. Bitcoin vs. Other Cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin Value and Price. Cryptocurrency Bitcoin. Table of Contents Expand.
What Determines Bitcoin's Price? Understanding What Determines Bitcoin's Price. Supply and Demand.
Cost of Production.