Are btc and btc the same thing
Contents:
Actively scan device characteristics for identification. Use precise geolocation data. Select personalised content. Create a personalised content profile. Measure ad performance. Select basic ads.
Bitcoin (BTC) Wallet
Create a personalised ads profile. Select personalised ads. Apply market research to generate audience insights.
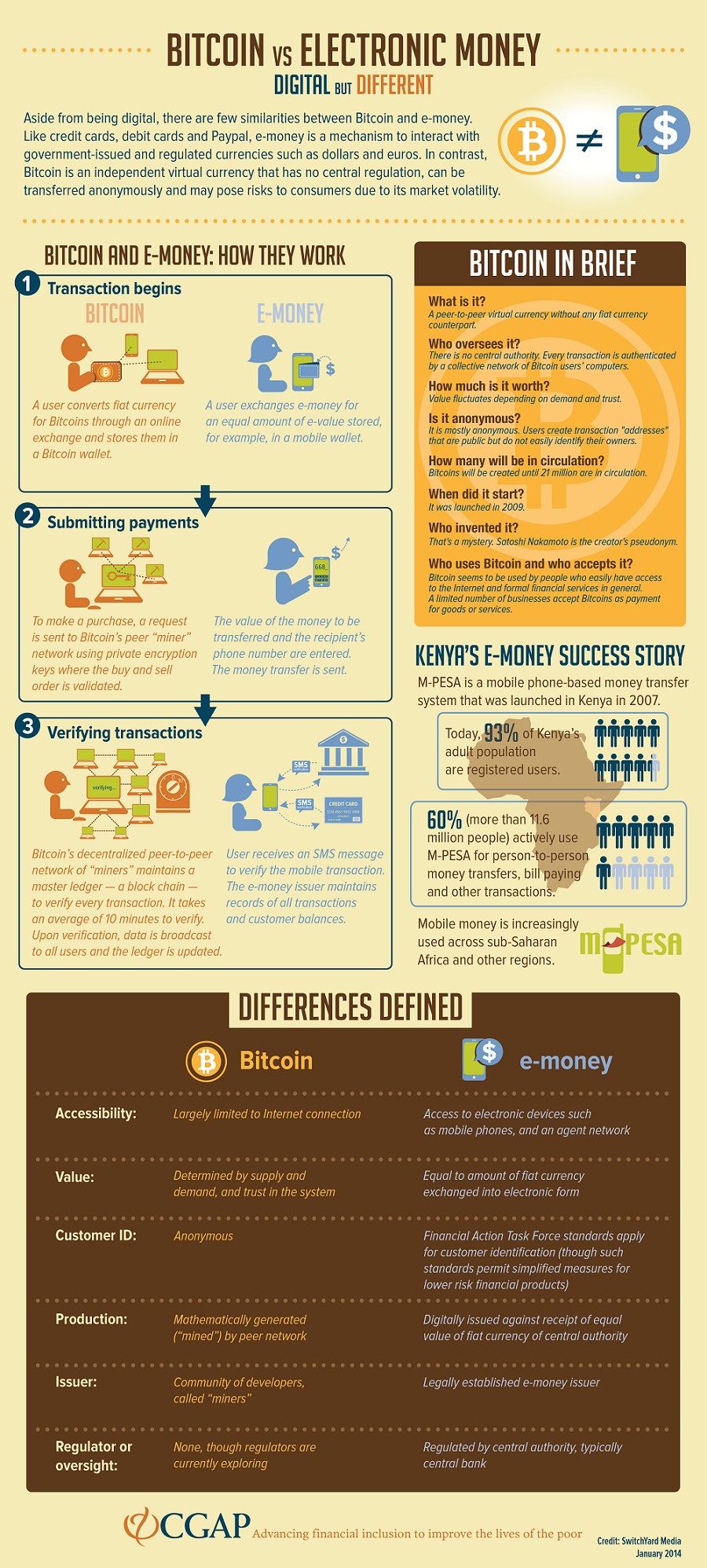
Measure content performance. Develop and improve products. List of Partners vendors. Transactions involving the digital currency bitcoin are processed, verified, and stored within a digital ledger known as a blockchain.
Powered by Finance Unlocked
Blockchain is a revolutionary ledger-recording technology. It makes ledgers far more difficult to manipulate because the reality of what has transpired is verified by majority rule, not by an individual actor.
Retrieved 1 July Download as PDF Printable version. Bitcoin has been criticized for its use in illegal transactions, the large amount of electricity used by miners, price volatility, and thefts from exchanges. Take a look! To change or withdraw your consent choices for Investopedia. Retrieved 13 March Coinbase is one of the more popular exchanges.
Additionally, this network is decentralized; it exists on computers all over the world. Popular credit card company Visa, Inc. V , for instance, processes close to million transactions per day, averaging roughly 1, transactions per second. The company's capability actually far surpasses that, at 65, transaction messages per second. How many transactions can the bitcoin network process per second? As the network of bitcoin users has grown, waiting times have become longer because there are more transactions to process without a change in the underlying technology that processes them.
Foodtech startup Grocemania announces nationwide expansion
Developers and cryptocurrency miners have come up with two major solutions to this problem. The first involves making the amount of data that needs to be verified in each block smaller, thus creating transactions that are faster and cheaper, while the second requires making the blocks of data bigger, so that more information can be processed at one time.
What is on-chain governance? On-chain governance is a governance system for blockchain in which rules are hardcoded into protocol. Bitcoin is a digital or. A quick summary of the key differences To finish up, let's recap why blockchain and Bitcoin are two completely separate things: Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, while blockchain is a distributed database. Bitcoin is powered by blockchain technology, but blockchain has found many uses beyond Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Cash BCH developed out of these solutions. Below, we'll take a closer look at how bitcoin and BCH differ from one another. Signature data has been estimated to account for up to 65 percent of data processed in each block, so this is not an insignificant technological shift.
Talk of doubling the size of blocks from 1 MB to 2 MB ramped up in and , and, as of February , the average block size of bitcoin increased to 1. By January , however, block size has declined back toward 1 MB on average. In September , research released by cryptocurrency exchange BitMex showed that SegWit implementation had helped increase the block size, amid a steady adoption rate for the technology.
- Bitcoin: What is it?;
- are bitcoin legal in uae.
- bitcoin with paypal credit.
- Bitcoin, cryptocurrency, blockchain... So what does it all mean?.
- GET UP TO $132;
Bitcoin Cash is a different story. Bitcoin Cash was started by bitcoin miners and developers equally concerned with the future of the cryptocurrency and its ability to scale effectively. However, these individuals had their reservations about the adoption of a segregated witness technology. They felt as though SegWit2x did not address the fundamental problem of scalability in a meaningful way, nor did it follow the roadmap initially outlined by Satoshi Nakamoto , the anonymous party that first proposed the blockchain technology behind cryptocurrency. Furthermore, the process of introducing SegWit2x as the road forward was anything but transparent, and there were concerns that its introduction undermined the decentralization and democratization of the currency.
In August , some miners and developers initiated what is known as a hard fork , effectively creating a new currency: BCH. BCH has its own blockchain and specifications, including one very important distinction from bitcoin.
In , the maximum block size for BCH was increased 4x to 32MB, but actual block sizes on Bitcoin cash have remained only a small fraction of the 32MB limit. Bitcoin Cash is thus able to process transactions more quickly than the Bitcoin network, meaning that wait times are shorter and transaction processing fees tend to be lower. The Bitcoin Cash network can handle many more transactions per second than the Bitcoin network can. However, with the faster transaction verification time comes downsides as well.
One potential issue with the larger block size associated with BCH is that security could be compromised relative to the Bitcoin network. Similarly, bitcoin remains the most popular cryptocurrency in the world as well as the largest by market cap, so users of BCH may find that liquidity and real-world usability is lower than for bitcoin. The debate about scalability, transaction processing, and blocks has continued beyond the fork which led to Bitcoin Cash. In November of , for example, the Bitcoin Cash network experienced its own hard fork, resulting in the creation of yet another derivation of bitcoin called Bitcoin SV.
Bitcoin SV was created in an effort to stay true to the original vision for bitcoin that Satoshi Nakamoto described in the bitcoin white paper while also making modifications to facilitate scalability and faster transaction speeds. Home Blockchain Explained The difference between blockchain and Bitcoin.
- Bitcoin Wallet | Bitcoin / BTC / Mining / Satoshi | imToken.
- Types of Bitcoin and Where to Buy Them.
- What is the difference between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash? – Blockchain Support Center.
- Bitcoin Cash VS Bitcoin: Which One Should You Choose.
- transfer litecoin to bitcoin wallet;
Many people wrongly conflate the two. Do you know the difference? Understanding Libra Understand how Facebook leveraged specific aspects of blockchain technology to launch a new cyrptocurrency called Libra, and its potential impact on the banking and finance sector. The Bitcoin Origin Story In late , around the time of the financial crisis, a ground-breaking post appeared on a little-known internet forum entitled Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system.
Blockchain Explained Jump to another post in the Blockchain Explained series but clicking on one of the tiles below. What is Blockchain? Learn what blockchain is and why there is so much hype around it.
What's the difference between blockchain and Bitcoin?
How transactions get into the blockchain. Understand the process to authenticate and authorise a transaction. The risks with public blockchains. Understand the three main risks associated with public blockchains. How blockchain data is stored and secured. As more and more blocks are added, how does the data remain manageable? The rise of private blockchains. What banks and businesses are using private blockchains today and why? Euromoney Learning On-Demand Powered by Finance Unlocked The world's first on-demand video learning platform designed by finance professionals, for finance professionals.