Bitcoin transaction private public key
Contents:
This creates a few complications, as the hashed form of an uncompressed key is different than the hashed form of a compressed key, so the same key works with two different P2PKH addresses. For this reason, Bitcoin Core uses several different identifier bytes to help programs identify how keys should be used:. Private keys meant to be used with compressed public keys have 0x01 appended to them before being Base encoded. See the private key encoding section above. These prefix bytes are all used in official secpk1 documentation.
The hierarchical deterministic key creation and transfer protocol HD protocol greatly simplifies wallet backups, eliminates the need for repeated communication between multiple programs using the same wallet, permits creation of child accounts which can operate independently, gives each parent account the ability to monitor or control its children even if the child account is compromised, and divides each account into full-access and restricted-access parts so untrusted users or programs can be allowed to receive or monitor payments without being able to spend them.
This means that two or more independent programs which agree on a sequence of integers can create a series of unique child key pairs from a single parent key pair without any further communication. Moreover, the program which distributes new public keys for receiving payment can do so without any access to the private keys, allowing the public key distribution program to run on a possibly-insecure platform such as a public web server.
Child public keys can also create their own child public keys grandchild public keys by repeating the child key derivation operations:.
Private and Public Keys
Whether creating child public keys or further-descended public keys, a predictable sequence of integer values would be no better than using a single public key for all transactions, as anyone who knew one child public key could find all of the other child public keys created from the same parent public key. Instead, a random seed can be used to deterministically generate the sequence of integer values so that the relationship between the child public keys is invisible to anyone without that seed.
The HD protocol uses a single root seed to create a hierarchy of child, grandchild, and other descended keys with unlinkable deterministically-generated integer values. The parent chain code is bits of seemingly-random data. The index number is a bit integer specified by the program. In the normal form shown in the above illustration, the parent chain code, the parent public key, and the index number are fed into a one-way cryptographic hash HMAC-SHA to produce bits of deterministically-generated-but-seemingly-random data.
The seemingly-random bits on the righthand side of the hash output are used as a new child chain code. The seemingly-random bits on the lefthand side of the hash output are used as the integer value to be combined with either the parent private key or parent public key to, respectively, create either a child private key or child public key:.
Specifying different index numbers will create different unlinkable child keys from the same parent keys. Repeating the procedure for the child keys using the child chain code will create unlinkable grandchild keys. Because creating child keys requires both a key and a chain code, the key and chain code together are called the extended key. An extended private key and its corresponding extended public key have the same chain code. The top-level parent master private key and master chain code are derived from random data, as illustrated below.
- Navigation menu!
- how to send coinbase bitcoin!
- up btc diet merit list!
- carvertical bitcoin talk.
- Blockchain Public Key & Private Key: A Detailed Guide.
- Public Key Cryptography and Cryptocurrency?
A root seed is created from either bits, bits, or bits of random data. This root seed of as little as bits is the only data the user needs to backup in order to derive every key created by a particular wallet program using particular settings. Warning: As of this writing, HD wallet programs are not expected to be fully compatible, so users must only use the same HD wallet program with the same HD-related settings for a particular root seed.
The root seed is hashed to create bits of seemingly-random data, from which the master private key and master chain code are created together, the master extended private key. The master extended keys are functionally equivalent to other extended keys; it is only their location at the top of the hierarchy which makes them special. Hardened extended keys fix a potential problem with normal extended keys.
If an attacker gets a normal parent chain code and parent public key, he can brute-force all chain codes deriving from it. If the attacker also obtains a child, grandchild, or further-descended private key, he can use the chain code to generate all of the extended private keys descending from that private key, as shown in the grandchild and great-grandchild generations of the illustration below. Perhaps worse, the attacker can reverse the normal child private key derivation formula and subtract a parent chain code from a child private key to recover the parent private key, as shown in the child and parent generations of the illustration above.
For this reason, the chain code part of an extended public key should be better secured than standard public keys and users should be advised against exporting even non-extended private keys to possibly-untrustworthy environments.
This can be fixed, with some tradeoffs, by replacing the normal key derivation formula with a hardened key derivation formula. The normal key derivation formula, described in the section above, combines together the index number, the parent chain code, and the parent public key to create the child chain code and the integer value which is combined with the parent private key to create the child private key.
The hardened formula, illustrated above, combines together the index number, the parent chain code, and the parent private key to create the data used to generate the child chain code and child private key. This formula makes it impossible to create child public keys without knowing the parent private key. Because of that, a hardened extended private key is much less useful than a normal extended private key—however, hardened extended private keys create a firewall through which multi-level key derivation compromises cannot happen.
Because hardened child extended public keys cannot generate grandchild chain codes on their own, the compromise of a parent extended public key cannot be combined with the compromise of a grandchild private key to create great-grandchild extended private keys. The HD protocol uses different index numbers to indicate whether a normal or hardened key should be generated. Index numbers from 0x00 to 0x7fffffff 0 to will generate a normal key; index numbers from 0x to 0xffffffff will generate a hardened key.
What Are Public Keys and Private Keys?
Bitcoin developers typically use the ASCII apostrophe rather than the unicode prime symbol, a convention we will henceforth follow. This compact description is further combined with slashes prefixed by m or M to indicate hierarchy and key type, with m being a private key and M being a public key. The following hierarchy illustrates prime notation and hardened key firewalls. Wallets following the BIP32 HD protocol only create hardened children of the master private key m to prevent a compromised child key from compromising the master key.
As there are no normal children for the master keys, the master public key is not used in HD wallets.
All other keys can have normal children, so the corresponding extended public keys may be used instead. The HD protocol also describes a serialization format for extended public keys and extended private keys. For details, please see the wallet section in the developer reference or BIP32 for the full HD protocol specification.
Root seeds in the HD protocol are , , or bits of random data which must be backed up precisely. It is used in elliptic curve cryptography as a means of producing a one-way function, which is a function that is easy to compute in one direction, but difficult to do so in the opposite direction. In cryptocurrency systems such as Bitcoin, this one-way function takes the private key as an input to generate the public key, which is the output.
Because of this, owners of a private key can confidently distribute their public key with the knowledge that no one will be able to reverse the function, and calculate the private key from the public key. A cryptocurrency address is simply a string of alphanumerical characters that a user can share with anyone that wants to send them money. As mentioned before, a cryptocurrency address is effectively a representation of the public key. An address is derived from the public key through the use of a one-way cryptographic hash function.
Beginning with the public key, this string of values is first ran through the SHA hashing algorithm to produce a hash, and then that hash is computed using RIPEMD to produce a bitcoin address.
Are private keys transmitted in a bitcoin transaction?
The bitcoin address, and addresses in other cryptocurrency systems, are what often appears in a transaction between two parties, with the address signifying the recipient of the funds. The private key consists of alphanumerical characters that give a user access and control over their funds to their corresponding cryptocurrency address. The private key is used to sign transactions that allow the user to spend their funds.
- Cryptopedia!
- Symmetric key cryptography vs asymmetric key cryptography?
- transfer litecoin to bitcoin wallet!
- Blockchain Public Key & Private Key: A Detailed Guide - Mycryptopedia.
- plus500 bitcoin wallet.
- Bitcoin Private Keys, Public Keys, and Addresses: The Basics.
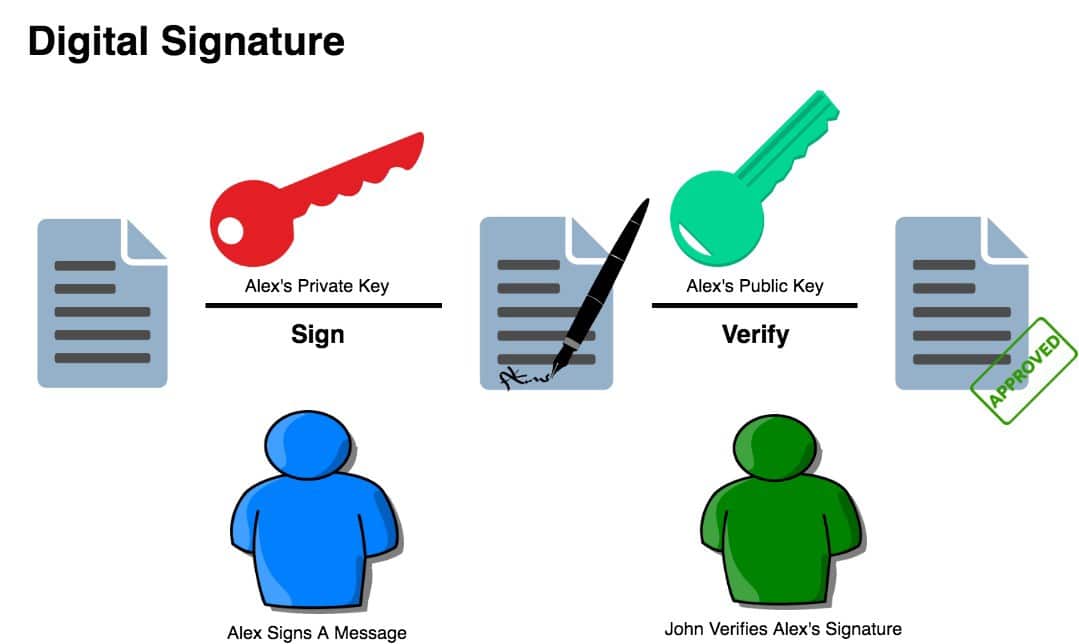
In other words, the private key creates unique digital signatures for every transaction that enable a user to spend their funds, by proving that the user does in fact have ownership of those funds. This signature can only be produced by someone with knowledge of the private key, which in this case is Bob. However, anyone with access to the public key and digital signature can use these two elements to verify that Bob does in fact exercise ownership over those 5 bitcoins. A digital signature is a mathematical scheme that is used for showing the authenticity of a digital message or document.
A digital signature that is valid will give the recipient of a digital message or document reason to believe that the message or document was in fact created by a known sender. A digital signature also indicates that the sender cannot in any way deny having sent the message or document, and that the message or document was not altered at any point while it was in transit. Digital signatures play an important role in cryptocurrency systems, because they prove ownership of funds and allow the individual in control of those funds to spend them.
If you hold your own private keys, consider modern HD wallets, which can do a great job of managing your private keys, and remember to never share them.
If you choose a custodial solution like an exchange, make sure you choose a trusted, reputable company that places high emphasis on security and regulation. Cryptopedia does not guarantee the reliability of the Site content and shall not be held liable for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies. The opinions and views expressed in any Cryptopedia article are solely those of the author s and do not reflect the opinions of Gemini or its management. The information provided on the Site is for informational purposes only, and it does not constitute an endorsement of any of the products and services discussed or investment, financial, or trading advice.
– The goal of public and private keys is to prove that a spent transaction was indeed signed by the owner of the funds, and was not forged. –. Bitcoin, as well as all other major cryptocurrencies that came after it, is built upon public-key cryptography, a cryptographic system that uses.
A qualified professional should be consulted prior to making financial decisions. Please visit our Cryptopedia Site Policy to learn more. Cryptopedia Staff. Is this article helpful? Public and Private Keys.
What are public and private keys?
Most cryptocurrencies have a pair of public and private keys that are used to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions. Though they both work together, from a secur Although fairly intuitive, sending and receiving bitcoin and crypto is different than using a credit card, Venmo, or PayPal to transfer funds. But once you've l Summary Public and private keys are an integral part of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Contents What is Public Key Cryptography?
The steps for someone to send you a transaction are: A transaction is encrypted using a public key. Public and Private Keys Control Your Crypto How public and private keys work together is fundamental to understanding how cryptocurrency transactions function. Author Cryptopedia Staff.